Single stranded, biotinylated DNA was captured on Streptavidin-coated agarose beads followed by derivatization with oligreen, a fluorescent dye. The assay protocol comprised the following steps:
#1 Capture streptavidin-coated agarose beads in the flow cell
#2 Perfusion of bead layer by biotinylated DNA, followed by perfusion of captured DNA by oligreen
#3 Monitoring of DNA derivatization by fluorescence measurement
#4 Removal of spent beads by flow reversal
DNA Assay by Fluorescence Spectroscopy
3.3.12.
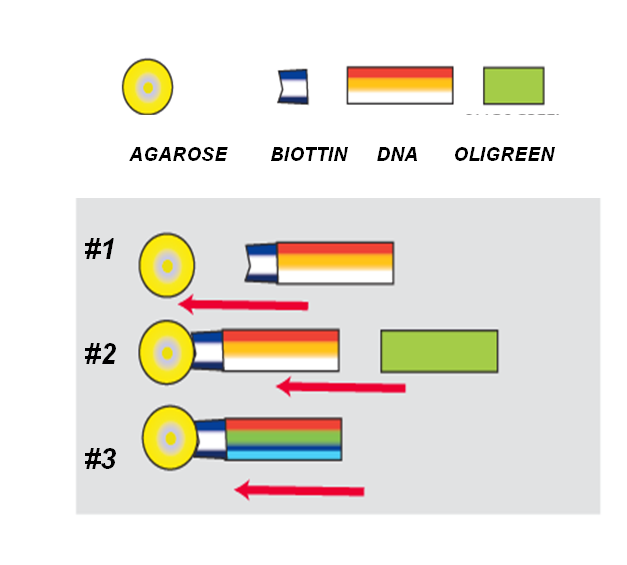
The goal of this method was to develop assay of telomerase, an enzyme that selectively extends ssDNA. The capture of b-ssDNA on beads would ensure separation of extended b-ssDNA from other DNA molecules and its accumulation on beads, while bead derivatization with oligreen will allow a sensitive detection, thus eliminating presently needed telomer amplification to repeat the protocol. Note that the beads must be discarded after each assay cycle since the biotine-streptavidine bond cannot be broken. The detection limit of 111pg DNA using BI fluorescence measurement.